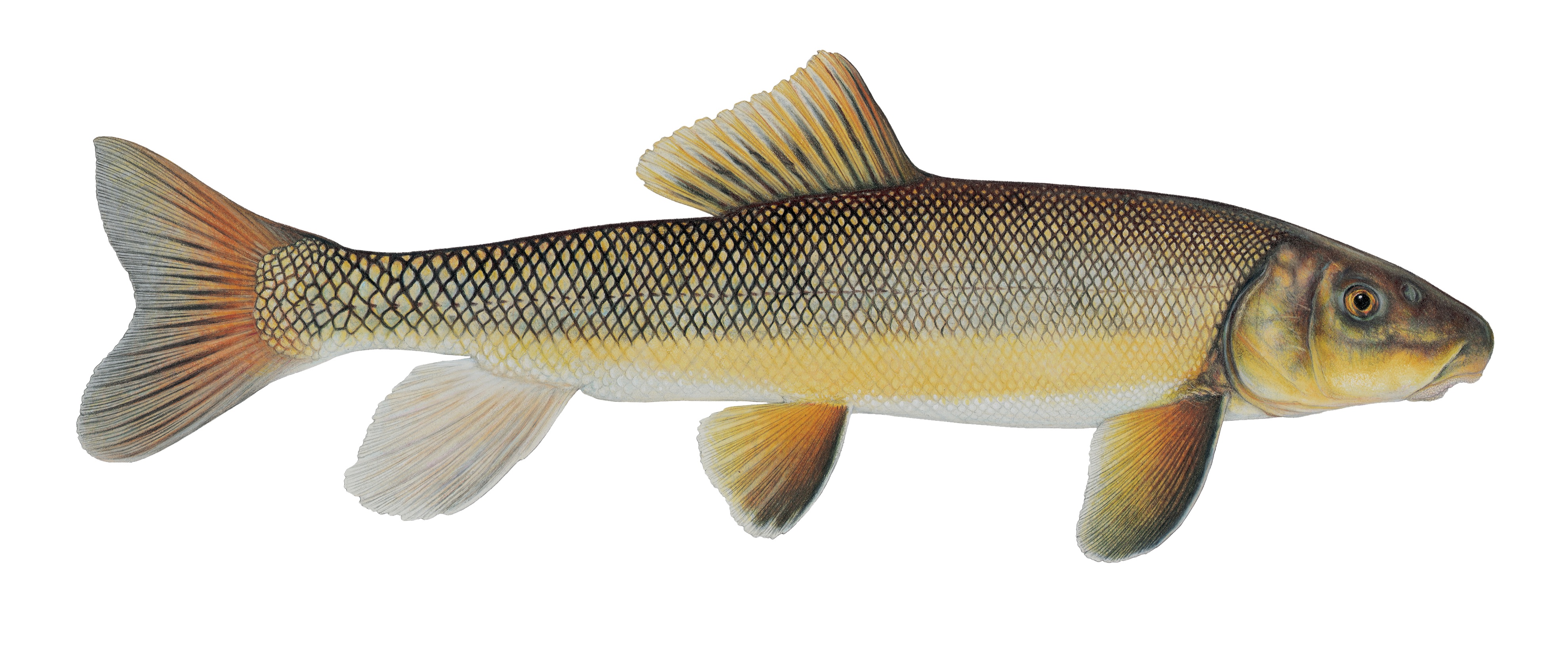
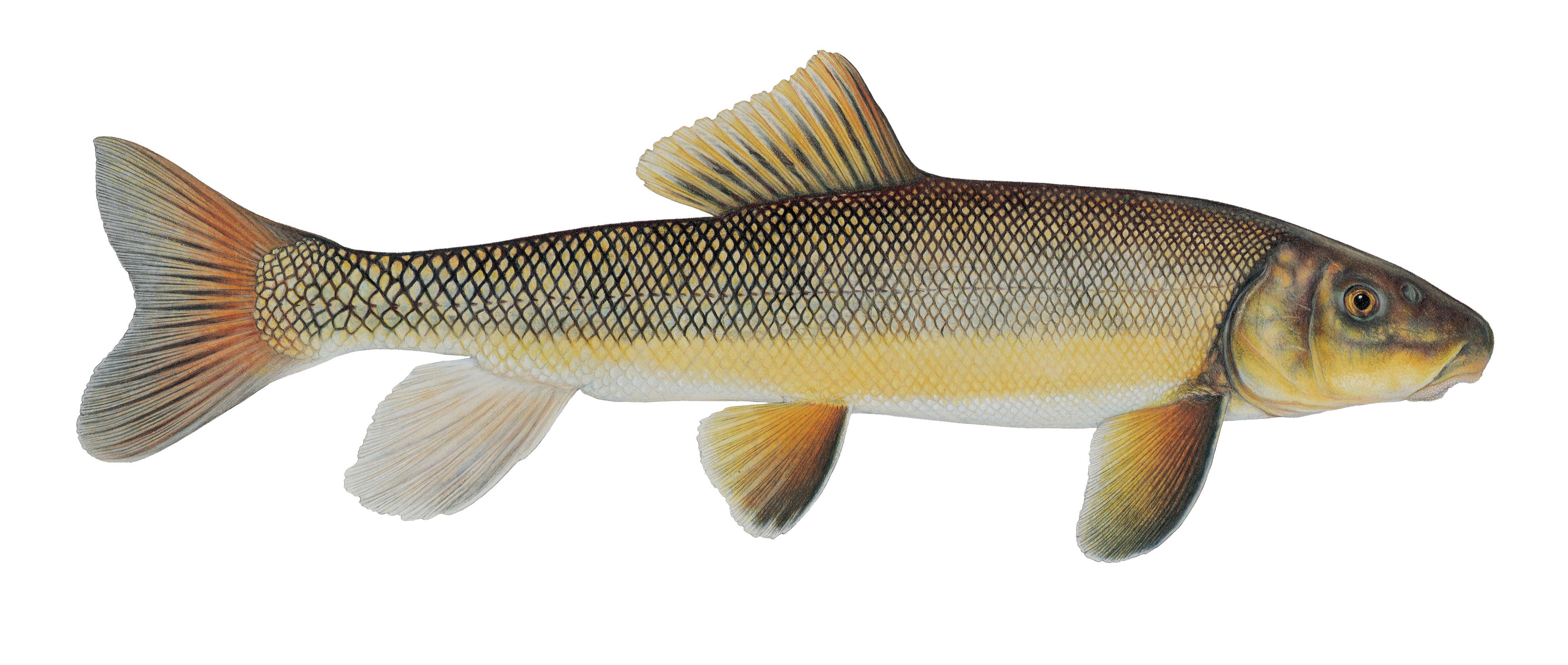
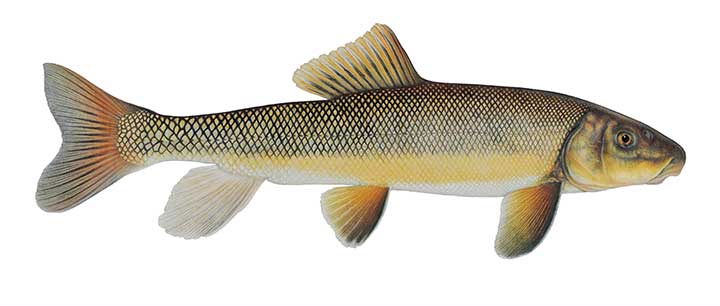
Suckers belong to the Catostomidae family. Members of this family are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia. Longnose suckers are members of the Catostomus genus.
Suckers
The mouths of suckers are on the underside of their heads. The thick, fleshy lips help them feed on detritus and bottom dwelling organisms. Like other native fish, suckers play an important role in the Jocko.

Click on a topic to learn more
- Other Names
Salish Name
The Salish call the longnose sucker Čɫen̓e
Scientific Name
Catostomus catostomus
Common Names
Finescale sucker - Classification
- Average Size
The typical longnose sucker in the Jocko River is 12 to 13 inches, although they can reach 22 inches.
- Life History
In the springtime, spawning migrations into small tributaries are common and males develop bright red colors on their bodies. Longnose sucker males become sexually mature in 4 years, females in 5 years. They spawn from April to early July when the water is 54-59° F. Incubation takes 10 to 20 days.
- Diet
The diet of longnose suckers is mostly algae but also includes midge larvae and most aquatic invertebrates.
- Habitat
Longnose suckers like cold, clear streams and lakes and sometimes moderately warm waters and turbid waters. They spawn over loose gravel beds in riffle areas.
- Status
Longnose sucker populations are doing well.
- Other Facts
The sucker with the greatest statewide distribution is the longnose sucker. It is found in all three of our major drainages and from mountainous streams to plains reservoir habitats. Longnose suckers are also one of the most frequently caught fish by Montana anglers.
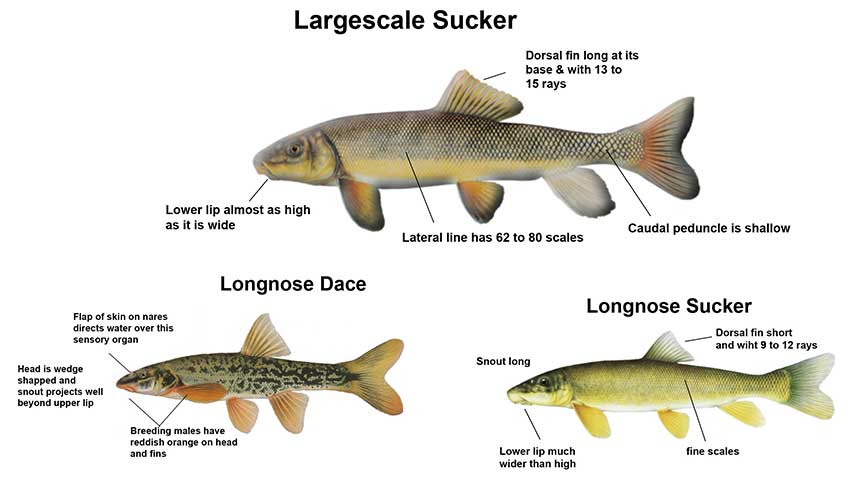
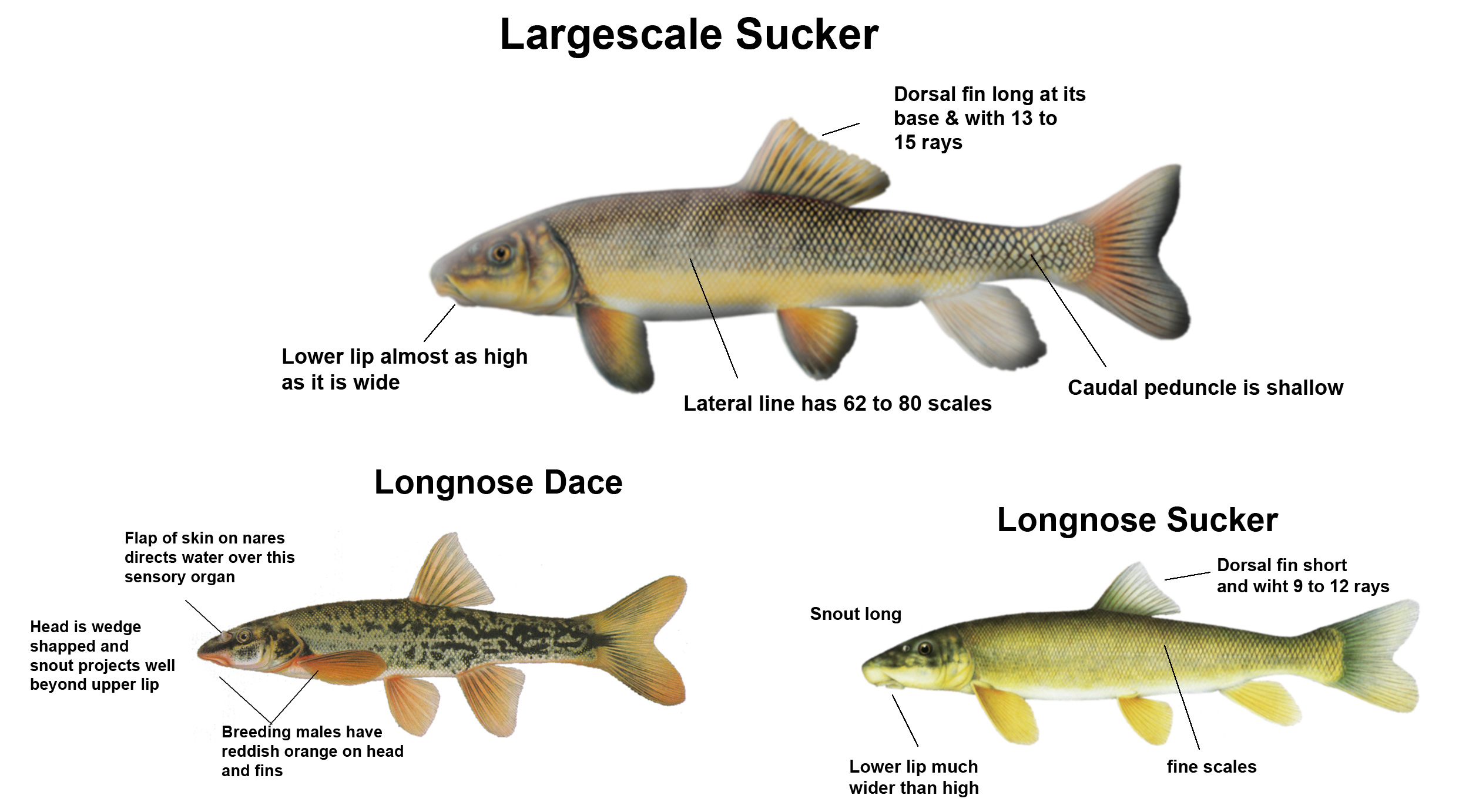
Rollover a letter to learn how to identify a Longnose Sucker

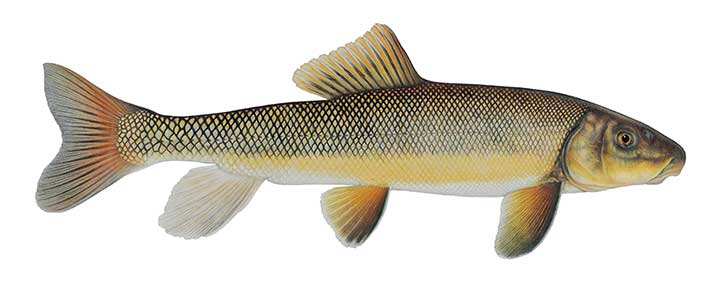
Click on a topic to learn more
- Other Names
Salish Name
The Salish name for largescale sucker is Sl̓aw̓s
Scientific Name
Catostomus macrocheilus
Common Names
Coarsescale sucker - Classification
Suckers belong to the Catostomidae family. Members of this family are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia. Largescale suckers are members of the Catostomus genus.
- Average Size
The typical largescale sucker in the Jocko River is 14 inches, although they can reach 22 inches.
- Life History
Largescale suckers become sexually mature in 4 to 5 years, although some males mature in 3 years. They spawn in April and May, migrating upstream, to reach gravel riffles with strong currents. Some spawn along lake margins. Their eggs stick to the bottom and hatch in 2 weeks.
- Diet
Largescale suckers are bottom feeders. They eat aquatic insect larvae, crustaceans, snails, algae, detritus, etc. Young suckers feed primarily on plankton.
- Habitat
Largescale suckers live in lakes and in pools and runs of medium to large rivers. They are usually found in shallow water, but sometimes can be found as deep as 80 feet. Fry move to shallows to feed by day and into deeper water at night.
- Status
Largescale sucker populations are doing well.
- Other Facts
The life span of a largescale sucker may be up to 11 years. Predators of young suckers include fish and fish eating birds, and in shallow waters, adults are preyed on by large mammals like bears and birds like eagles and ospreys.
Largescale suckers have decreased in abundance below Libby Dam due to colder water temperatures delaying spawning.
Rollover a letter to learn how to identify a Largescale Sucker
Suckers
The mouths of suckers are on the underside of their heads. The thick, fleshy lips help them feed on detritus and bottom dwelling organisms. Like other native fish, suckers play an important role in the Jocko.

Click on a topic to learn more
- Other Names
Salish Name
The Salish call the longnose sucker Čɫen̓e
Scientific Name
Catostomus catostomus
Common Names
Finescale sucker - Classification
Suckers belong to the Catostomidae family. Members of this family are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia. Longnose suckers are members of the Catostomus genus.
- Average Size
The typical longnose sucker in the Jocko River is 12 to 13 inches, although they can reach 22 inches.
- Life History
In the springtime, spawning migrations into small tributaries are common and males develop bright red colors on their bodies. Longnose sucker males become sexually mature in 4 years, females in 5 years. They spawn from April to early July when the water is 54-59° F. Incubation takes 10 to 20 days.
- Diet
The diet of longnose suckers is mostly algae but also includes midge larvae and most aquatic invertebrates.
- Habitat
Longnose suckers like cold, clear streams and lakes and sometimes moderately warm waters and turbid waters. They spawn over loose gravel beds in riffle areas.
- Status
Longnose sucker populations are doing well.
- Other Facts
The sucker with the greatest statewide distribution is the longnose sucker. It is found in all three of our major drainages and from mountainous streams to plains reservoir habitats. Longnose suckers are also one of the most frequently caught fish by Montana anglers.
Rollover a letter to learn how to identify a Longnose Sucker


Click on a topic to learn more
- Other Names
Salish Name
The Salish name for largescale sucker is Sl̓aw̓s
Scientific Name
Catostomus macrocheilus
Common Names
Coarsescale sucker - Classification
Suckers belong to the Catostomidae family. Members of this family are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia. Largescale suckers are members of the Catostomus genus.
- Average Size
The typical largescale sucker in the Jocko River is 14 inches, although they can reach 22 inches.
- Life History
Largescale suckers become sexually mature in 4 to 5 years, although some males mature in 3 years. They spawn in April and May, migrating upstream, to reach gravel riffles with strong currents. Some spawn along lake margins. Their eggs stick to the bottom and hatch in 2 weeks.
- Diet
Largescale suckers are bottom feeders. They eat aquatic insect larvae, crustaceans, snails, algae, detritus, etc. Young suckers feed primarily on plankton.
- Habitat
Largescale suckers live in lakes and in pools and runs of medium to large rivers. They are usually found in shallow water, but sometimes can be found as deep as 80 feet. Fry move to shallows to feed by day and into deeper water at night.
- Status
Largescale sucker populations are doing well.
- Other Facts
The life span of a largescale sucker may be up to 11 years. Predators of young suckers include fish and fish eating birds, and in shallow waters, adults are preyed on by large mammals like bears and birds like eagles and ospreys.
Largescale suckers have decreased in abundance below Libby Dam due to colder water temperatures delaying spawning.
Rollover a letter to learn how to identify a Largescale Sucker
Suckers
The mouths of suckers are on the underside of their heads. The thick, fleshy lips help them feed on detritus and bottom dwelling organisms. Like other native fish, suckers play an important role in the Jocko.

Click on a topic to learn more
- Other Names
Salish Name
The Salish call the longnose sucker Čɫen̓e
Scientific Name
Catostomus catostomus
Common Names
Finescale sucker - Classification
Suckers belong to the Catostomidae family. Members of this family are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia. Longnose suckers are members of the Catostomus genus.
- Average Size
The typical longnose sucker in the Jocko River is 12 to 13 inches, although they can reach 22 inches.
- Life History
In the springtime, spawning migrations into small tributaries are common and males develop bright red colors on their bodies. Longnose sucker males become sexually mature in 4 years, females in 5 years. They spawn from April to early July when the water is 54-59° F. Incubation takes 10 to 20 days.
- Diet
The diet of longnose suckers is mostly algae but also includes midge larvae and most aquatic invertebrates.
- Habitat
Longnose suckers like cold, clear streams and lakes and sometimes moderately warm waters and turbid waters. They spawn over loose gravel beds in riffle areas.
- Status
Longnose sucker populations are doing well.
- Other Facts
The sucker with the greatest statewide distribution is the longnose sucker. It is found in all three of our major drainages and from mountainous streams to plains reservoir habitats. Longnose suckers are also one of the most frequently caught fish by Montana anglers.
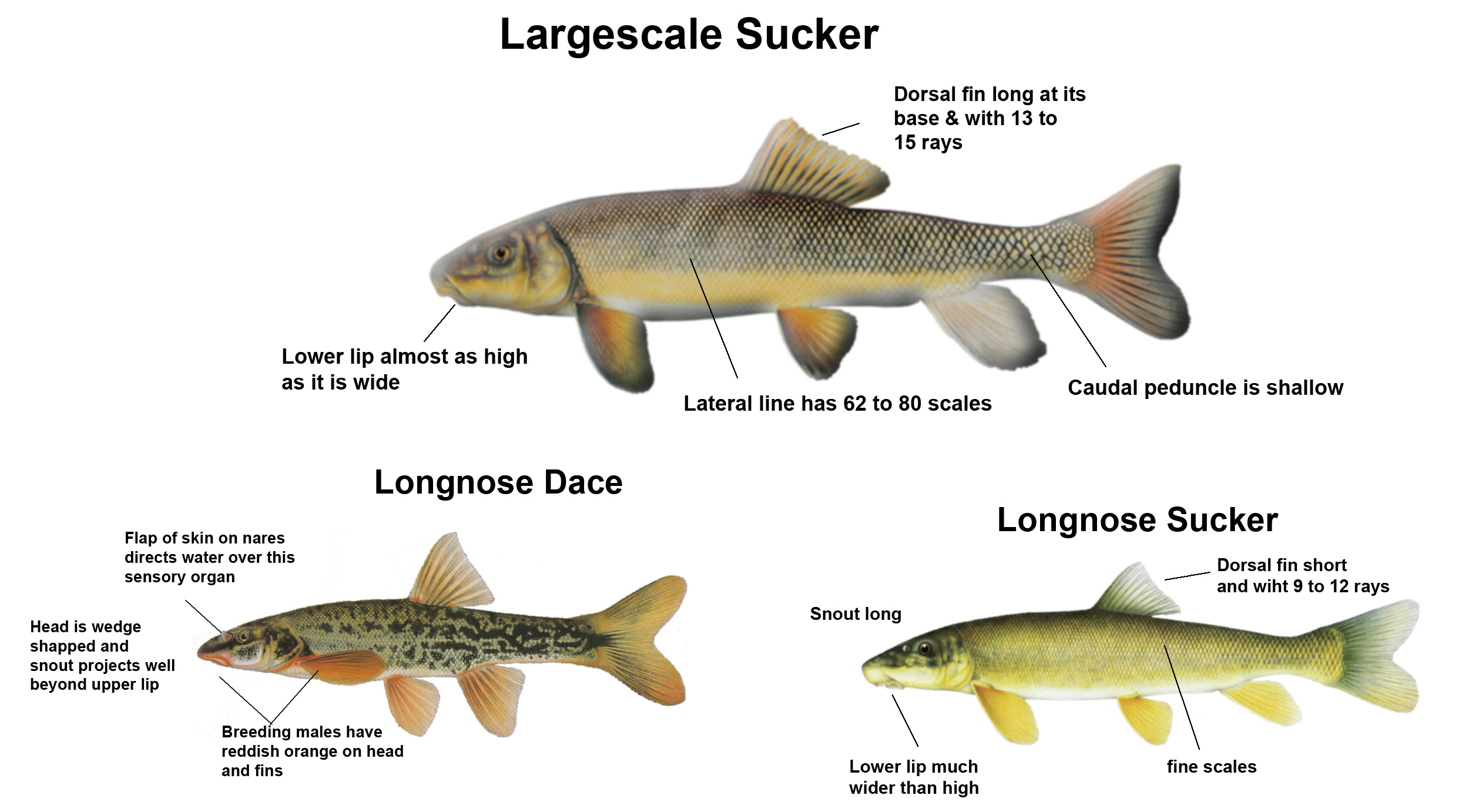
Rollover a letter to learn how to identify a Longnose Sucker


Click on a topic to learn more
- Other Names
Salish Name
The Salish name for largescale sucker is Sl̓aw̓s
Scientific Name
Catostomus macrocheilus
Common Names
Coarsescale sucker - Classification
Suckers belong to the Catostomidae family. Members of this family are found in North America, east central China, and eastern Siberia. Largescale suckers are members of the Catostomus genus.
- Average Size
The typical largescale sucker in the Jocko River is 14 inches, although they can reach 22 inches.
- Life History
Largescale suckers become sexually mature in 4 to 5 years, although some males mature in 3 years. They spawn in April and May, migrating upstream, to reach gravel riffles with strong currents. Some spawn along lake margins. Their eggs stick to the bottom and hatch in 2 weeks.
- Diet
Largescale suckers are bottom feeders. They eat aquatic insect larvae, crustaceans, snails, algae, detritus, etc. Young suckers feed primarily on plankton.
- Habitat
Largescale suckers live in lakes and in pools and runs of medium to large rivers. They are usually found in shallow water, but sometimes can be found as deep as 80 feet. Fry move to shallows to feed by day and into deeper water at night.
- Status
Largescale sucker populations are doing well.
- Other Facts
The life span of a largescale sucker may be up to 11 years. Predators of young suckers include fish and fish eating birds, and in shallow waters, adults are preyed on by large mammals like bears and birds like eagles and ospreys.
Largescale suckers have decreased in abundance below Libby Dam due to colder water temperatures delaying spawning.
Rollover a letter to learn how to identify a Largescale Sucker
© 2021 Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes | Contact Us
© 2021 Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes | Contact Us